There’s no denying how popular chocolate is.
John Q. Tullius even said, “nine out of ten people love chocolate. The tenth person always lies.”
That being said, odds are pretty good you’re a chocolate lover too (even if that statistic isn’t exactly accurate). Here’s a more accurate one:
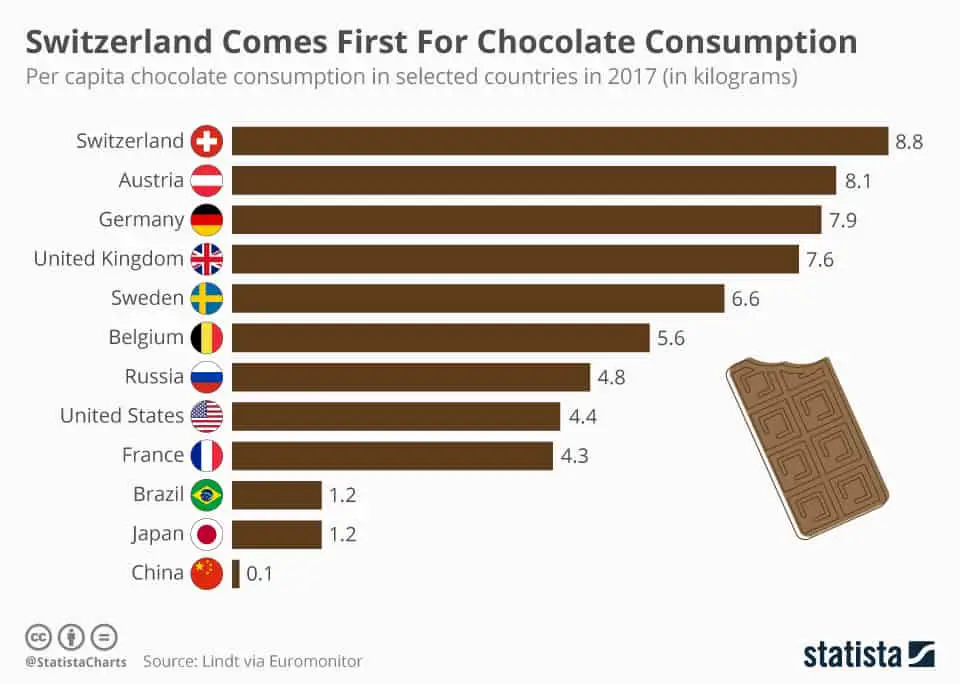
However, how much do you actually know about the chocolate you’re buying?
What’s in your chocolate?
How is the production of the chocolate that you’re eating affecting the world around you?
The thing about chocolate is that it’s consumed in incredible quantities around the world. In 2016, it was estimated that retail sales of chocolate amounted to roughly $98.2 billion.
Additionally, even though cocoa originated in Mexico and Central America, almost 75 percent of the world’s supply of cocoa is actually produced in Africa.
These stats should give you pause as to the impact that chocolate production might have on not just the environment, but on human lives.
Fortunately, there’s a way to ensure that the chocolate you’re buying was produced in a responsible and ethical manner – and that’s by buying chocolate that’s been fair trade certified.
The Importance of Knowing What’s in Your Chocolate
Whether or not the chocolate you’re eating will benefit your health depends a great deal on what’s actually in your chocolate.
If you’re eating chocolate candy bars that have dozens of other ingredients in them, you’re probably not getting any health benefits out of it.
However, if you’re eating chocolate made with high percentages of cocoa in moderation, you’re more likely to benefit from its consumption.
As such, if you have a craving for chocolate, make sure you choose the healthier option.
How Do You Choose the Right Chocolate?
As previously discussed, chocolate can be both good for you or bad for you. While moderation is a key factor, so are the ingredients found in the chocolate that you’re eating.
Whether or not the chocolate is made and distributed in an eco-friendly manner should also be considered when choosing the right chocolate.
What Ingredients Should You Avoid?
Unfortunately, a huge amount of chocolate that’s produced is made using incredibly unhealthy ingredients.
For example, the name brand chocolate candy bars found near the check-out counters of grocery stores are typically packed with additives.
As a general rule, you should just stick to dark chocolate. With that in mind, the following are some of the unhealthy ingredients commonly used in chocolate:
Artificial Flavoring
Artificial flavors are chemicals that were synthesized to taste like natural flavors.
While there’s no proof that artificial flavors are less healthy than natural flavors, there’s a good chance that the product as a whole isn’t very healthy for you.
Chocolate (and food in general) that’s highly processed tends to use a lot of artificial flavoring.
It’s also important to note that manufacturers only have to list artificial flavors as “artificial flavors,” which is incredibly vague.
As such, consider artificial flavoring an indicator that the chocolate probably isn’t very healthy as a whole.
Artificial Sweeteners
Cocoa by itself is actually quite bitter. Many manufacturers add artificial sweeteners, such as sucralose and saccharin, to their chocolate to make it sweet.
However, these sweeteners have been linked to weight gain.
Some sweeteners, such as aspartame, has even been found to increase the risk of chronic fatigue, headaches, diabetes, Parkinson’s, multiple sclerosis, and much more – despite being approved by the FDA.
High Fructose Corn Syrup
Although also an artificial sweetener, high fructose corn syrup deserves its own mention.
This is because it’s made from genetically modified (GMO) corn and is found in almost all processed foods as a cost-effective alternative to real sugar.
High fructose corn syrup has been linked to all kinds of health issues, including diabetes, weight gain, obesity, fatty liver disease, and inflammation, which can increase the risk of heart disease and cancer as well as exacerbate gout.
Partially Hydrogenated Oils
Partially hydrogenated oils are used to increase the shelf life of food.
The way partially hydrogenated oil is produced is through a process in which hydrogen is added to unsaturated fat to turn it into a solid fat.
It’s also known as trans fat. Partially hydrogenated oils can also increase bad cholesterol and lower good cholesterol.
Preservatives
Preservatives are added to help prevent food products from spoiling.
Some of the common preservatives found in chocolate include BHA (butylated hydroxyanisole) and BHT (butylated hydroxytoluene), both of which are linked to issues with the brain’s neurological system.
Unfortunately, these aren’t the only unhealthy additives that are often found in chocolate.
Other ingredients found in chocolate that you should shy away from include carrageenan, hydrolyzed vegetable proteins, propylene glycol, sodium benzoate, sodium lactate, and much more.
What Ingredients Are in Good Quality Chocolate?
Considering the many unhealthy ingredients commonly used in the production of chocolate, you might be wondering what kind of chocolate could possibly be healthy.
Fortunately, it’s the main ingredient of chocolate – cocoa – that gives it its health benefits.
The thing is, the more ingredients that are added to the chocolate, the less cocoa there will be, thereby diminishing its potential health benefits.
Because of this, you’ll want to look for chocolate that was made with at least 70 percent cocoa.
This also means that you’ll want to choose a dark chocolate option. Cocoa butter is also an acceptable alternative to cocoa since it’s a derivative of cocoa.
If you notice ingredients such as a vanilla extract or essential oils have been added to the chocolate, that’s usually nothing to worry about.
It generally means that they were used to add to the flavor as an alternative to much less healthy artificial flavor and colors.
There’s going to be sugar added to the chocolate no matter what. Even dark chocolate with over 80 percent cocoa content will have some sugar.
Of course, you’ll want to choose a chocolate that limits how much sugar it adds. Usually, the more cocoa is in the chocolate, the less sugar it has.
Just make sure that the sugar that’s used is real. For example, some of the healthier chocolate options will often use cane sugar.
Some manufacturers may also add milk fat – some milk fat is fine. It’s chocolate in which milk is added that you probably shouldn’t eat too much of.
When it comes down to it, the more cocoa that there is in the chocolate and the fewer additional ingredients that the chocolate has, the healthier it probably is.
Are the Ingredients Environmentally-Friendly?
Let’s say that you’ve found a chocolate bar that has no unhealthy additives and contains a high percentage of cocoa. Great!
Odds are that it will be beneficial to your health (if, once again, you eat it in moderation). But was it produced in an environmentally-friendly way?
The following are a few ways to tell whether the chocolate you’re about to devour is bad for the environment or not:
Organic Chocolate
Cocoa beans are like any other crop in that they are often farmed with the use of pesticides.
One study found that cocoa beans from 16 different farms in Ghana were contaminated with numerous pesticides.
Although the concentration of pesticides found did not exceed the European Union Maximum Residue Limits for cocoa beans, you’re better off buying organic chocolate if you don’t want to consume pesticide residue.
However, depending on where the cocoa was sourced, certified organic cocoa is not always an option. There are many smaller scale farms who use sustainable farming practices that cannot afford to be certified organic.
For example, just because their cocoa isn’t organic doesn’t mean that they’re using pesticides that can harm the environment as well as the farmers working in the cocoa fields.
What does this mean?
It means that if the chocolate contains organic ingredients – great! However, you may not want to dismiss the chocolate altogether if the cocoa isn’t “certified organic,” as it may still be environmentally friendly.
Fortunately, there are other ways to determine whether the cocoa is environmentally-friendly or not.
Recycled Packaging
The packaging used in chocolate is often not very eco-friendly. You can reduce your environmental footprint even more by buying chocolate that’s packaged using materials that were recycled and that are recyclable.
Some chocolate manufacturers have gone even further by investing in compostable packaging materials.
Rainforest Alliance Certification
Chocolate manufacturers that are certified by the Rainforest Alliance have met stringent standards in regard to environmental practices.
Farms producing cocoa beans must meet natural resource conservation, human well-being, biodiversity conversation, and effective planning and farm management systems standards.
Essentially, buying chocolate that’s Rainforest Alliance certified ensures that you’re supporting responsible farming practices.
Fair Trade Certification
Fair trade certification requires producers to meet a number of different standards, including environmental standards.
If you’re wondering whether or not Fair Trade chocolate is actually fair, check out our article here.
These standards encourage farmers to practice more sustainable farming. For example, chocolate that is fair trade will not be made with GMO-produced cocoa.
5 Sustainable Fair Trade Chocolate Brands
Keeping in mind everything that fair trade attempts to accomplish, the following are five chocolate brands that are certified fair trade and that contribute to social and environmental causes in more than one way.
When purchasing chocolate from these brands, you can feel confident in the fact that you are buying fair trade chocolate that involves zero child labor and that is legitimately “fair.”
Not to mention, these chocolate brands are quite tasty, too!
1. Alter Eco
Alter Eco is a Certified B-Corporation that has built a reputation over the past decade and a half for its high-quality chocolate and its dedication to social and environmental issues.
Alter Eco chocolate products
Alter Eco has a variety of chocolate products available, from bars to truffles. Many of their chocolate bars, including their Deepest Dark Super Blackout bar, contain 90 percent cocoa.
Many of their truffles are also made with a large percentage of cocoa, such as their Superdark Truffles, which have 80 percent cocoa.
No matter how much cocoa is used, all of their chocolate products are made with certified organic, non-GMO ingredients.
They even use coconut oil as a sustainable alternative to palm oil. Their chocolate is fair trade certified and their ingredients are sourced from fair trade farmers in the Dominican Republic, Peru, Ecuador, Sri Lanka, Bolivia, Indonesia, and India.
It’s worth noting that while many of their chocolate products are 100 percent certified fair trade, there are a few exceptions.
This is because some of their products contain a few ingredients, such as milk and sea salt, that aren’t regulated by an international fair trade standard.
However, they do work closely with their chocolatiers to ensure that such ingredients are sourced from sustainable suppliers.
The Alter Eco Difference
Alter Eco strives to make a positive social and environmental impact on the world. The following are a few examples of how they are achieving this:
-
Replanting the Peruvian rainforest – Working with the PUR Project and their cacao partner, Acopagro Coop, Alter Eco is working to replant and conserve a portion of the Peruvian Amazon.
This has helped boost biodiversity, improve the food security of the coop, and improve the quality and yield fo the co-op’s crops.
Additionally, the number of trees planted every year accounts for more than 100 percent of Alter Eco’s carbon expenditure.
-
Compostable or recyclable packaging – Alter Eco is committed to using recyclable or compostable packaging for all of their products by the end of 2020.
For example, their chocolate bars are already wrapped in recyclable aluminum foil and FSC-certified paper, while their truffles come in compostable wrappers.
They are constantly looking for additional solutions to make their packaging more sustainable.
-
Local community activism – Alter Eco encourages its employees to give back to the community by allowing them to take three paid work days per year to support a cause of their choice within their community.
This cause can range from cleaning up a local beach to planting trees in a local park.
Alter Eco Awards
- 2016 Best Bite Aware by Delicious Living
- 2016 Best Packaging by Nexty
- 2014 Environmental Stewardship award by Whole Foods Market
- 2012 Business Environmental Award by Acterra
2. Equal Exchange
Equal Exchange has been selling high-quality coffee and chocolate products for over three decades. However, what makes Equal Exchange unique is the fact that they are a co-op.
Equal Exchange has over 120 worker-owners, all of whom have an equal stake in the company as well as an equal vote.
They believe that they should expect no less of themselves than what is demanded of their farmer partners throughout the world.
They have worked with small farmer organizations since they were established in 1986, including farmer organizations in Africa, Asia, Latin America, and the U.S..
As one of the largest democratic worker co-ops in the country, every worker-owner at Equal Exchange has one vote as well as the right to serve as leader, to speak their mind, and to request information about the company.
Basically, it means that top-level managers and entry-level employees have the same share and the same say in the company and receive an equal share of profits or losses.
There is one thing that’s important to mention: Equal Exchange challenges the existing trade model and therefore is not “certified” as fair trade by any of the larger fair trade organizations.
They believe that certifiers are tailored to the needs of big corporations and do not favor small scale farmers.
However, they are 100 percent fair trade – their chocolate meets the minimum fair trade standards, all of their suppliers are regularly audited against fair trade standards, and they actually pay more for their cocoa than any fair trade premium requires.
Equal Exchange Chocolate
Although more well-known for their coffee, Equal Exchange has many different chocolate products to choose from as well, including bars, mini-bars, chocolate chips, and hot cocoa mix.
The amount of cacao used in these products varies. For example, they do have some milk chocolate products that have 43 percent cacao, but they also have an Organic Total Eclipse Dark Chocolate bar made with 92 percent cacao.
The majority of their products use ingredients that are 100 percent fair trade certified as well as certified organic.
They source their cacao from small-scale farmers in Peru and their sugar from small-scale farmers in Paraguay.
The Equal Exchange Difference
Besides being closely aligned with small-scale farmers as a result of being a co-op, Equal Exchange also partners with many other organizations.
For example, their Interfaith Program has partnered Equal Exchange with thousands of churches, temples, and communities of faith across the U.S.
Equal Exchange also works with several grant partners to support small farmers, including the USAID Cooperative Development Program and RSF Social Finance.
Equal Exchange Awards
- 2017 Massachusetts Sustainable Business of the Year by the Sustainable Business Network
- 2012 Best Support of the Fair Trade Movement by the Fair Trade Resource Network
- The 2009 Green Business Award by the City of Boston
- 2006-2008 World’s Most Democratic Workplaces by WorldBlu
3. Theo
Founded in 2005, Theo Chocolate has the distinction of being the first organic, fair trade certified chocolate maker in North America.
While many chocolate brands have individual products that were certified fair trade, Theo Chocolate’s entire business was certified fair trade by Fair for Life in 2010.
When it comes to being a fair trade partner, Theo Chocolate is about as transparent as you can be.
All of their facilities as well as the facilities of their suppliers are audited every year to ensure fair wages, acceptable working conditions, and minimal environmental impact.
While producers have to be audited to be a fair trade partner, buyers rarely verify their own practices through a yearly audit.
Theo Chocolate is also very transparent about all of their ingredients and where they come from – in fact, you can read profiles about the farming cooperatives they source their ingredients from on their website.
Theo Chocolate provides helpful information, such as how much of their ingredients they source from each co-op, how many farms are part of the collective, and more.
They even make a point to visit their suppliers on a yearly basis and try to make sure that the farmers they work with actually get a chance to taste the chocolate being made from their beans.
Theo Chocolate Products
Theo Chocolate sells a large collection of confections as well as chocolate products that include chocolate bars, chocolate cups, chocolate drinks, and chocolate for baking. All of their ingredients are certified organic, kosher, fair trade, and non-GMO.
For example, their Pure Dark chocolate bar is made with 85 percent cocoa beans along with cane sugar, cacao butter, and ground vanilla bean, all of which are certified fair trade and organic.
They source their cane sugar from Brazil and its cocoa from small farms in the Dominican Republic and Peru.
The Theo Chocolate Difference
They are also incredibly involved when it comes to trying to make the world a better place.
Some of the causes that they actively participate in and contribute to include the Eastern Congo Initiative, the Vitalogy Foundation, the Special Olympics, FareStart, Mary’s Place, Food Lifeline, ROOTS Young Adult Shelter, and The National Association of Women Business Owners.
Theo Chocolate Awards
- The 2014 Progressive Grocers Award by Top Women in Grocery
- The 2016 Community Impact Award for Sustainability in Business Operations by Seattle Business Magazine
- The 2017 Clean Choice Award by Clean Eating Magazine
4. Divine
Like Equal Exchange, what makes Divine unique amongst the majority of chocolate brands is that they were founded in 1998 by a coop of over 100,000 cocoa farmers in Ghana.
The co-op (the Kuapa KoKoo Farmers’ Union) now owns 44 percent of the company and shares in its profits.
The farmers have a real voice in how the business is run. Two representatives of the co-op are Directors on the Divine Chocolate Board and one out of the four yearly board meetings is held in Ghana.
Divine is also certified as a B-Corporation.
Divine Chocolate Products
Divine is another chocolate brand that boasts incredibly high-quality chocolate products full of natural non-GMO ingredients that are certified fair trade.
Despite the fact that they have a wide variety of different chocolate flavors, they do not use any artificial flavors, palm oil, or soy ingredients and they use 100 percent pure cocoa butter.
Their Exquisitely Rich Dark Chocolate bar consists of 85 percent cocoa and is 99 percent fair trade certified. Its ingredients include cocoa mass, cocoa butter, cocoa powder, vanilla, sugar, and sunflower lecithin.
Other popular bars include their Dark Chocolate with Refreshing Lemon and their Dark Chocolate with Cocoa Nibs.
Although Divine works with a co-op called CECAQ-11 from São Tomé that supplies cocoa within the organic certified range, Divine’s core range is not certified organic.
However, most Kuapa Kokoo farmers do not use pesticides and rely largely on natural crop protection methods.
However, Divine is constantly looking for ways to reduce their environmental footprint. For instance, they are striving to create more sustainable packaging for their products, such as by using little to no plastic and by only using FSC paper and board.
The Divine Difference
In addition to the fact that the co-op receives 44 percent of Divine’s distributable profits, Divine also invests two percent of its annual revenue to support co-op projects, such as women empowerment.
In fact, not only are both Divine and the coop run by women, but a third of the co-op itself consists of women.
Divine works to empower women by encouraging and mentoring women in Ghana in many different ways, such as teaching classes on adult literacy and numeracy.
Divine Awards
- 2015 Sustainable Business Award for Social Impact Innovation by Guardian
- 2008 Favourite Fairtrade Product by Good Housekeeping
- 2008 Best Ethical Business by Observer
- 2007 Best Social Enterprise by Observer
5. Endangered Species
Endangered Species is one of the most unique chocolate brands out there.
This is because Endangered Species was founded with the goal of contributing to conservation in order to support wildlife and habitats in need.
Founded in 1993, Endangered Species has become a leader in ethical chocolate. In fact, they were the first American chocolate bar line that could fully trace their cacao beans from farm to bar.
Endangered Species Chocolate Products
Endangered Species has become known for crafting premium chocolate made from ingredients that are non-GMO and certified fair trade by FLO.
Although they mostly offer chocolate bars, they do have a few other chocolate products, such as truffles and chocolate bites.
What’s particularly of note is that all of their chocolate products are made with at least 60 percent cocoa.
Their darkest option is their Panther chocolate bar, which is made with 88 percent cocoa. Other ingredients include cane sugar, soy lecithin, vanilla, and chocolate liquor. The bar is certified fair trade, gluten-free, non-GMO, and vegan.
The Endangered Species Difference
In addition to supporting small-scale farmers by being fair trade certified, Endangered Species makes significant contributions to various conservation programs.
They do this by donating 10 percent of their annual net profits to a variety of organizations (each of which is guaranteed a minimum annual donation of $10,000).
Over the past three years, they have generated over $1.4 million in donations. The following are some of the current and past partners that Endangered Species has worked with:
- The National Forest Foundation
- The Dian Fossey Gorilla Fund
- African Wildlife Federation
- Xerces Society
- SEE turtles
- Chimp Haven
- Rainforest Trust
- Wildlife Conservation Network
Chocolate Brands That Are Not 100 Percent Fair Trade
The previously mentioned chocolate brands are brands that were established with the goal of being socially and environmentally responsible in mind.
This is not the case with the majority of chocolate brands out there.
Some of the biggest chocolate companies in the world didn’t become fair trade certified until it began affecting their public perception.
And it’s these brands that are typically not 100 percent fair trade – or even anywhere close to it.
Many of these brands may source some of their cocoa from fair trade partners. For example, both Mars and Nestle source less than half of their cocoa from fair trade certified producers.
As such, don’t just look for the fair trade label – check the actual percentage of the ingredient that is certified fair trade.
Is Chocolate Good for You?
Before we delve further into the production of chocolate and the impact it can have on the environment and on local communities, let’s figure out whether chocolate is something you should be buying at all. After all, sugary treats are rarely good for you.
If you’re eating chocolate that’s packed with additives, then you’re in for a rude awakening – such consumption of chocolate has been linked with coronary heart disease, hypertension, and diabetes.
Eating too much chocolate that’s overly processed and filled with additives is likely to lead to weight gain as well.
However, if you eat chocolate in moderation and it doesn’t contain unhealthy ingredients, then there are actually quite a few health benefits to be had from it.
The Benefits of Eating Chocolate
As long as you eat chocolate with a high percentage of cocoa, such as dark chocolate, you’ll receive some health benefits.
It’s milk chocolate that you should watch out for, since this is the type of chocolate that tends to have the most unhealthy additives and which tends to use less cocoa as a result.
Dark chocolate, while healthier than milk chocolate, does still contain extra calories, fat, and sugar.
This means that eating chocolate is only healthy for you if you do so in moderation. Eat too much of it, and it will likely have a negative effect on your health.
With that in mind, these are some of the potential health benefits of eating chocolate:
-
Chocolate contains healthy nutrients – Dark chocolate containing between 70 and 85 percent cocoa contains fiber, iron, magnesium, copper, manganese, potassium, selenium, phosphorus, and zinc.
-
Chocolate contains antioxidants – Dark chocolate is packed with antioxidants, such as flavanols and polyphenols.
-
Chocolate could reduce the risk of heart disease – Studies have indicated that cocoa powder can help to decrease oxidized LDL cholesterol in men as well as increase HDL and decrease the total LDL in people who have high cholesterol.
As a result, chocolate could potentially help to reduce the risk of heart disease.
Conclusion
Few people will argue that chocolate isn’t delicious.
But don’t you think that the chocolate you eat would taste a lot better knowing that its main ingredient, cocoa, is coming from a source that is socially, economically, and environmentally responsible?
By purchasing chocolate that is certified fair trade, you’ll be able to enjoy your chocolate with the knowledge that your money isn’t contributing to child labor and unsustainable farming practices.
You Might Also Like…
- Is Fast Food Bad for the Environment? (& What You Can Do)
- Is Fabric Softener Bad for the Environment? (+5 Eco-Friendly Options)
- Is Fuel Dumping Bad for the Environment? (& How Often It Happens)
- Is Electricity Generation Bad for the Environment? (What You Should Know)
- Is Dry Cleaning Bad for the Environment? (4 Surprising Facts)
- Is Diamond Mining Bad for the Environment? (Important Facts)
- Is DEET Bad for the Environment? 4 Effects (You Should Know)
- Is Cat Litter Bad for the Environment? (5 Common Questions)
- Is Burning Cardboard Bad for the Environment? (6 Facts)
- Is Burning Paper Bad for the Environment? (6 Surprising Facts)
- Is Burning Leaves Bad for the Environment? (7 Quick Facts)
- 4 Natural Cleaners for Quartz Countertops
- 6 Eco-Friendly Acrylic Paint Brands (For Sustainable Artists)
- 5 Eco-friendly Alternatives to Acrylic Paint (& How to Make Them)
- Is Acrylic Paint Bad for the Environment? (7 Quick Facts)
- Is Acrylic Yarn Bad for the Environment? 8 Crucial Facts
- Is Acrylic Bad for the Environment? (8 Quick Facts)
- Is Aluminum Foil Bad for the Environment? 7 Quick Facts
- Is Bleach Bad for the Environment? 6 Crucial Facts
- Is Lithium Mining Bad for the Environment? 6 Crucial Facts




































